The billions of dollars spent by firms such as IBM result in new successful products but also in products that never reach the marketplace or are unsuccessful in the marketplace. These are assets that cannot be separated from the company and are often difficult to quantify or value. Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
Leaseholds and Leasehold Improvements
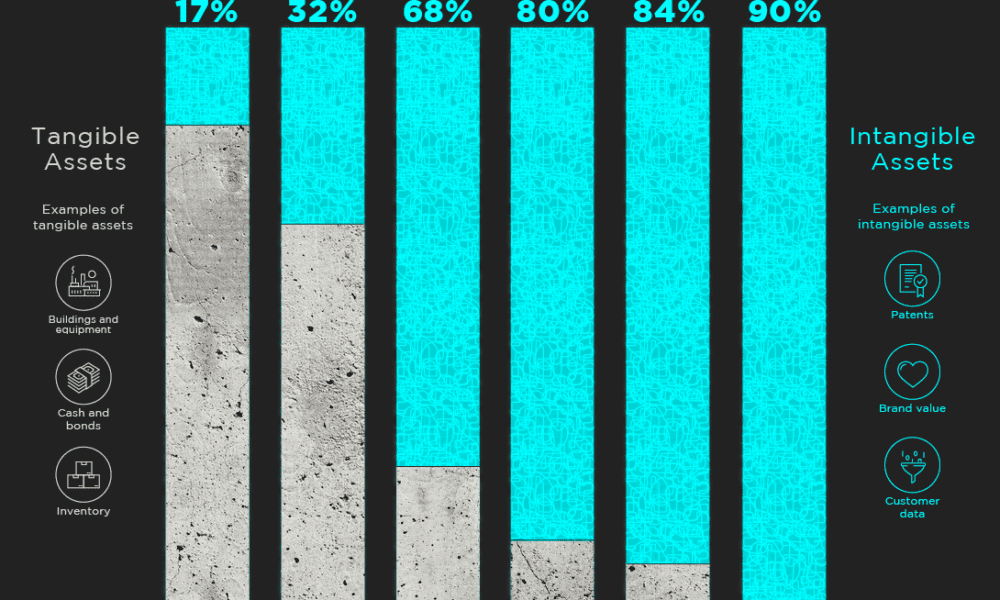
Current assets are recorded at the top of the statement and reflect the short-term assets of the company. Various types of assets could be considered tangible or intangible, some of which are short-term or long-term assets. In this article, we’ll define each in more depth as well as provide contrasting examples. Depletion also lowers the cost value of an asset incrementally through scheduled charges to income. Where it differs is that it refers to the gradual exhaustion of natural resource reserves, as opposed to the wearing out of depreciable assets or the aging life of intangibles. As this Journal entry shows, the purchase price is first allocated to the identifiable net assets based on their fair market value.
What Is Depreciation, Depletion, and Amortization (DD&A)?
Our solution has the ability to prepare and post journal entries, which will be automatically posted into the ERP, automating 70% of your account reconciliation process. Imagine a company, ABC Inc., acquires a patent for a new technology. The cost of obtaining the patent is $100,000, and the patent has a useful life of 10 years, the expensing of intangible assets is called and no residual value. The term amortization is used in both accounting and lending with different definitions and uses. For example, a consumer might be willing to pay $4.99 for a tube of Sensodyne toothpaste rather than to purchase the store brand’s sensitivity toothpaste for $3.59 despite it being the same and cheaper.
Amortization of Intangibles: Definition, Types, and Example
More depreciation expense is recognized earlier in an asset’s useful life when a company accelerates it. A business might buy or build an office building and use it for many years. The original office building may be a bit rundown but it still has value. The cost of the building minus its resale value is spread out over the predicted life of the building with a portion of the cost being expensed in each accounting year. Negative brand equity occurs when consumers are not willing to pay extra for a brand-name version of a product. In more practical terms, the way your small business records depreciation and amortization also differs.

A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. It represents the value today of the excess earnings of a particular enterprise. Excess earnings represent earnings above the normal earnings of an industry. These are the improvements made by the lessee to the leased property. They consist of such items as air conditioning, partitioning, and elevators. For this reason, the cost to the creator to obtain copyright is usually charged to an expense account when incurred.
Amortization of intangibles definition
Both the truck and the patent are used to generate revenue and profit over a particular number of years. Since the truck is a physical asset, depreciation is used, and since the rights are intangible, amortization is used. Assume, for example, that a construction company buys a $32,000 truck for contractor work, and that the truck has a useful life of eight years.
An asset that’s acquired by a company might have a long, useful life. It may provide benefits to the company over time, not just during the period in which it’s acquired. Amortization and depreciation are two main methods of calculating the value of these assets whether they’re company vehicles, goodwill, corporate headquarters, or patents. Straight-line amortization is calculated the same was as straight-line depreciation for plant assets.
Unlike tangible assets, which are subject to depreciation, intangible assets are often subject to amortization. A goodwill account appears in the accounting records only if goodwill has been purchased. A company cannot purchase goodwill by itself; it must buy an entire business or a part of a business to obtain the accompanying intangible asset, goodwill. Since these positive factors are not individually quantifiable, when grouped together they constitute goodwill. The amount of any goodwill impairment loss is to be recognized in the income statement as a separate line before the subtotal income from continuing operations (or similar caption). Amortization expense appears in the reporting entity’s income statement, usually within the selling, general and administrative cluster of expenses.
Cost of goods sold represents the costs directly involved with the production of a good. Tangible fixed assets, such as plant and equipment, are also recorded on the balance sheet but as their useful life is reduced, that portion is expensed on the income statement as depreciation. Amortization and depreciation both allocate the cost of an asset over its useful life. Amortization deals with intangible assets like patents and copyrights, while depreciation applies to tangible assets such as machinery and buildings. Both methods ensure accurate expense matching and financial reporting.
- An intangible asset like a brand name can be critical to a company’s long-term success.
- Amortization will however begin when it is determined that the useful life is no longer indefinite.
- Amortization spreads out the cost of the asset each year as it is expensed on the income statement.
- For example, the parent company of 7—Eleven Markets sells franchises to individual owner-operators.
- Privately-held organizations and nonprofits are allowed to amortize this goodwill asset to expense over a period not to exceed 10 years.
However, a recognizable brand name can still create significant value for a company. Investing in the quality of the product and a creative marketing plan can have a positive impact on the brand’s equity and the company’s overall viability. Amortization is similar to depreciation, but while depreciation applies to tangible assets (like buildings and machinery), amortization is used for intangible assets. The main goal is to match the expense of the asset with the revenue it generates over time, ensuring a more accurate representation of a company’s financial health.
HighRadius offers a cloud-based Record to Report Suite that helps accounting professionals streamline and automate the financial close process for businesses. We have helped accounting teams from around the globe with month-end closing, reconciliations, journal entry management, intercompany accounting, and financial reporting. Brand equity is an intangible asset and refers to a value premium that a company generates from a recognized product instead of its generic equivalent. Companies create brand equity for their products through mass marketing campaigns. The sum-of-the-years digits method is an example of depreciation in which a tangible asset such as a vehicle undergoes an accelerated method of depreciation. A company recognizes a heavier portion of depreciation expense during the earlier years of an asset’s life under this method.